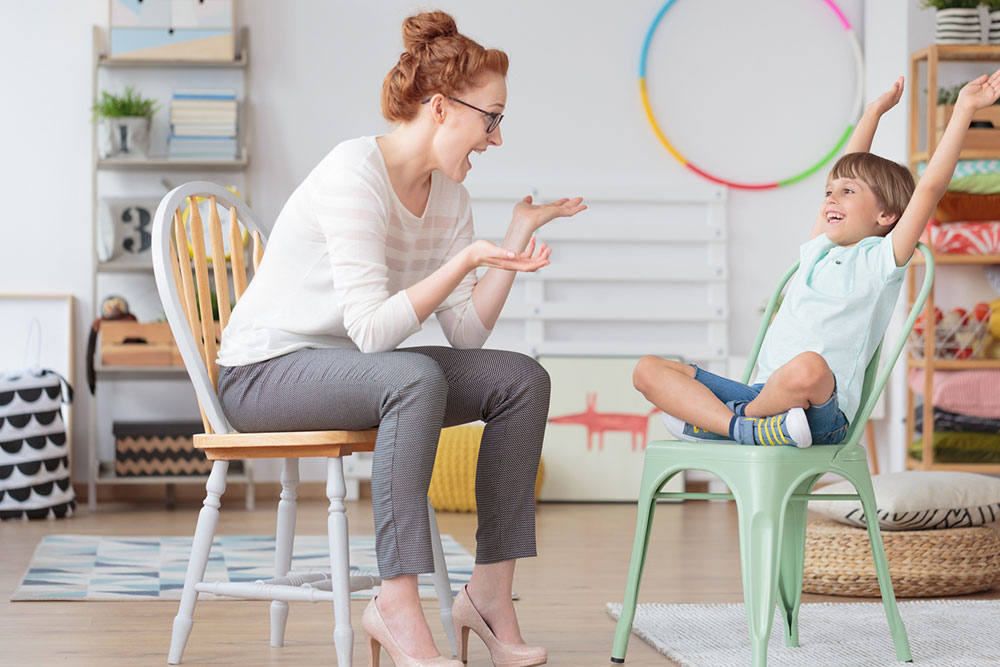
Lifestyle Changes to Manage ADHD
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, or ADHD, is a medical condition that impacts brain activity and associated development, focus, and impulse control. According to the ADD Research Center, ADHD affects roughly 6.4 million American children between the ages of 4- to 17-years of age and 4 percent of American adults. While many traditional doctors prescribe medications (i.e., Ritalin, etc.) to help manage the symptoms of ADHD, the following lifestyle changes may work in collaboration with medical treatments to help ADHD in both child and adult patients:
1. Support groups
Many ADHD patients suffer from the negative stigma that can greatly impact them in childhood and into adulthood. However, many therapists recommend seeking out an ADHD support group. ADHD support groups meet regularly and foster understanding, socialization, community, and friendships among ADHD patients and their loved ones.
2. Establish routine
The wandering mind and attention span of a patient with ADHD may also benefit from established routine. This may look different from patient to patient but may include physical and digital tools to help manage daily activities, tasks, and serve as a reminder to help day to day life run more smoothly and consistently. Try the following organizational tools:
- A day or digital planner for homework, work tasks, social obligations, bills, etc.
- A brightly colored calendar posted with the month’s to-dos to capture attention.
- A digital task list broken down into smaller items to prevent overwhelming the patient.
- A sleep routine, posted in the bathroom or bedroom to serve as a reminder of what to do before bedtime to unwind (i.e., scheduled quiet time for a hot bath, meditation, breathing exercises, journalling, reading, stretching, etc.).
3. Stress management
Stress and anxiety can be particularly intrusive for patients with ADHD so stress-busting techniques are encouraged to avoid exacerbating symptoms. Try mindful meditation, yoga, hiking, arts or crafts, or listening to relaxing music in order to unwind as you need it throughout the day and before bedtime.
4. Setting boundaries
Impulse control can be difficult for patients with ADHD, and often that means taking on too many obligations or projects to please others. However, too many responsibilities can leave someone with ADHD stressed out, overwhelmed, and fatigued. So aim to not only keep a schedule or calendar, but to say no if it’s getting too full.
5. Healthy ADHD diet
Even though what we eat or drink doesn’t cause ADHD, the foods and beverages we put into our bodies can worsen ADHD symptoms. For instance, studies link highly processed foods to greater rates of inattention and hyperactivity. Whereas whole foods like lean protein (i.e., poultry and fish), healthy fats (nuts, eggs, flaxseed, and avocados), whole grains (i.e., complex carbs, beans, and legumes) can support brain health and control blood sugar spikes that heighten ADHD symptoms.